The RSUM program calculates the left-hand, right-hand, trapezoidal, midpoint and SimpsonRiemann sums to estimate the value of a single integral of any reasonably well-behaved real-valued function. For example,
![]() .
.
The xi sample values are evenly spaced, with separation ![]() . Of course,both the sample values and the weights wi vary with the variety of sum; e.g., for a left-hand sum and for i=0,1,2,...,n-1,we have
. Of course,both the sample values and the weights wi vary with the variety of sum; e.g., for a left-hand sum and for i=0,1,2,...,n-1,we have ![]() ; so that wi = 1 and xi = a + i
; so that wi = 1 and xi = a + i![]() .
.
On entry, RSUM expects the following information on the stack:
level 5: Integrand
level 4: Independent variable (that is used in level 5)
level 3: Lower limit of integration
level 2: Upper limit of integration
level 1: Number of subdivisions
For example, to approximate ![]() by using 15 subdivisions, we would enter the following:
by using 15 subdivisions, we would enter the following:
level 5: 'LOG(1+T)/T'
level 4: 'T'
level 3: 1
level 2: 100
level 1: 15
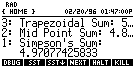
After running RSUM, the stack display on the right would appear.
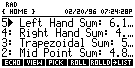
Scrolling up the stack (by using the up-arrow key), we would also discover: